ASIC Miner ICERIVER KAS KS0 Profitability In the realm of cryptocurrency mining, the Iceriver KAS KS0 miner has garnered widespread attention. Tailored specifically for the Kaspa network's KHeavyHash algorithm, it boasts high hashing power and low power consumption, making it an ideal choice for many miners. In this article, we will comprehensively assess IceRiver KS0 profitability while considering the Kaspa market conditions and the attributes of KS0 miner. Kaspa Market Dynamics Kaspa is a vibrant cryptocurrency network aimed at delivering high performance and scalability for everyday transactions. At the time of writing this article, the Kaspa coin trades at approximately $0.04959. But it's essential to note that cryptocurrency markets are highly susceptible to price volatility. Hence, investors must remain vigilant about market dynamics. Additionally, the Kaspa network's mining difficulty and reward mechanisms play a role in mining returns. Attributes of the IceRiver KS...
How to effectively prevent the harm of mining viruses to the computer?
Some terminals or servers are passively mined due to infection with mining Trojans. The main reason is the accidental download of virus-containing software and the implantation of mining Trojans because of high-risk vulnerabilities such as weak passwords in the device. So how can we deal with and prevent this virus? First, we need to understand the definition of cryptocurrency mining.
Definition of cryptocurrency mining
Cryptocurrency mining uses computer equipment resources (such as hash rate, network bandwidth, hard disk storage, etc.) to solve complex mathematical operations, thereby generating decentralized cryptocurrencies based on blockchain technology. Coins and Ethereum are the main ones, and cryptocurrencies can be bought and sold through the trading market, thereby obtaining many capital gains.
I. The harm of cryptocurrency mining to computers
Direct harm
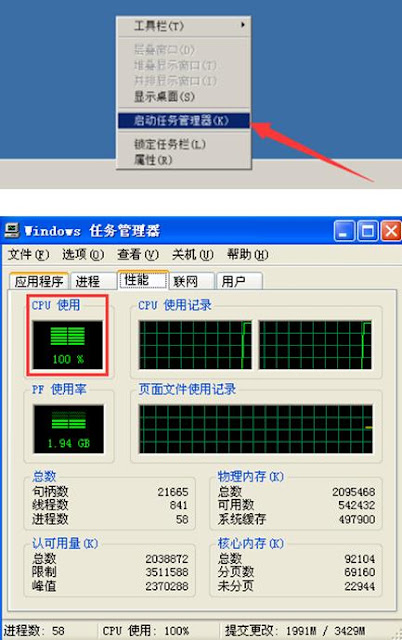
1. The host performs high-performance computing for a long time, wastes network bandwidth, occupies high CPU and memory, and cannot process normal user requests or tasks in time.
2. Increase power consumption and speed up computer CPU, memory, and other hardware aging speed.
Potential hazard
1. Hackers steal confidential information through mining programs, such as confidential documents, user names, passwords of crucial assets, etc., resulting in further losses to campus IT assets.
2. Hackers control the host as a broiler to attack other units on the Internet, violating the network security law.
3. Hackers use the already controlled machines as a springboard to continue infiltrating the business system area, resulting in more severe network security attacks.
II. The way to find the virus
1. Look at the process. In general, the process has a high CPU usage during mining operations. You can check the current operating process to see if there is a process with high CPU usage.
2. Check the security log. If the virus did not clean up the logs, traces could be found in some security logs. Find the abnormal login IP through the security log, and continue to search for viruses.
3. View historical commands. The history command might have some clues if it wasn't deleted. Find and download samples through the history command and execute the sample instructions.
4. Check the timing script. If you need to start the mining virus regularly, there will be some information in the timing script to check. First, find the virus by searching the timer crontab.
III. Disposal of mining viruses
1. Professional anti-virus software is installed on the computer, and an emergency check is performed on the terminal to verify whether the terminal is infected with a mining virus. The virus is checked by scanning the anti-virus software.
2. Some mining is found on the webpage. When the user visits the website linked to the horse, it is loaded into the browser for mining. When the browser is closed, the mining disappears, and the mining program will not stay on the original disk. Virus-checking tools cannot kill it. However, you can use TCP monitoring network software to check who is communicating with the mining pool server marked by the platform. After analysis, conduct killing and forensics, and then conduct targeted killing.
3. If you can't kill it, you can directly reinstall the system.
IV. Preventive measures
1. Install antivirus software
Install antivirus software, update the virus database, and perform antivirus.
2. Avoid weak passwords
Avoid weak passwords and avoid using the same password on multiple systems.
3. Close the application service
Turn off unnecessary services such as Windows Sharing Services, Remote Desktop Control, etc.
4. Application installation
Do not install unfamiliar and risky apps; try to download apps from regular app stores.
5. Raise awareness of cybersecurity
Do not use storage devices such as U disks and mobile hard disks of unknown origin.
Do not click on emails and attachments from unknown sources.
Do not download cracked software from unknown sources.
Do not access the public network and do not allow the internal network to access external network devices of unknown origin.
Epilogue
Finally, remind everyone when mining. Be sure to pay attention to these potential dangers to avoid unnecessary losses.






Comments
Post a Comment
Tell us your opinion